Describe the Process of Recycling Nutrients
Absorb nutrients N P. Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment ie.

Living World 3 Ecosystems 3 Clf Online Learning
The nutrients may be sedimentary and originate from soil or rocks or gaseous and originate from air or water.

. Nutrient cycles are a basic part of nature. Unfortunately urban expansion has thrown many of these cycles far out of balance. Plants then metabolically fix these nutrients into their growing biomass.
A nutrient cycle is a cyclic movement of nutrients from its major reservoir through different organisms back into the same reservoir. A method to recycle phosphate and nitrogen critical nutrients for algae cultivation has been developed by a team of scientists who describe this method. Plants require 13 essential nutrient elements 6 major 7 micronutrients and can profit from some beneficial nutrients.
Nutrients are present on the earth where they are recycled transformed into different forms and reutilized. There are also materials that are recycled via erosion weathering water drainage. Answer to Qi a Describe the process of recycling nutrients 4.
All the elemental matters tend to go through a cycle in the biosphere which is said to be an interconnected process that is said to be the biogeochemical cycle. The recycling process varies depending on what item is being recycled. Nutrient runoff and leaching can impact water bodies and soil quality around our communities.
So decomposers can recycle dead plants and animals and help keep the flow of nutrients available in the environment. Algae nutrient recycling is a triple win. Illustrated by Cheryl Bolinger-McKirnan Jim Hoorman OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION.
Protozoa and nematodes consume the nitrogen rich bacteria and help the nutrient recycling process. They release the nitrogen as ammonia. Nutrient cycling is a cyclic process that encompasses the movement of nutrients from the physical environment to living organisms and back to the environment.
N CO2 P. Nutrients lost to air and water. The process of recycling nutrients from the inorganic to organic and back to a living system is known as biogeochemical cycling.
Ammonia and soil nitrates are converted back and forth in the soil. Other members of the food chains re-use the nutrients assembled by plants. The paper is taken to a recycling plant where it is separated into different types and grades.
Decomposers can recycle dead plants and animals into chemical nutrients such as carbon and nitrogen that are released back into the soil air and water as food for living plants and animals. In other words recycling is the art of making waste into a resource. Many species that cause.
These cycles indicate the flow of nutrients in an ecosystem. What is Nutrient Recycling. The term nutrients refer mainly such type of elements chemical which living organisms plants and animals use as their food.
Nutrients constantly move from the environment to living organisms and back. A system in which process outputs or wastes are used as a system input or resource. There are basically four types of cycles that are present which handle the overall consumption and decaying of nutrients in the environment.
Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic. A nutrient cycle is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Without the presence of soil microorganisms CHONPS contained in soil organic.
Cycling here refers the continuous input and output of the nutrientIt is the worth considering that the word Biogeochemical recycling. Nitrogen and phosphorus are plant essential nutrients that are currently in excess in many aquatic ecosystems due to runoff from urban and agricultural areas. Improved vegetative cover land configuration management and alley farming will form the base for sustained production achieving better soil and moisture conservation and improved nutrient recycling.
Recycling Nutrients in the ecosystem is important because only plants can create new nutrients by combining molecules from the soil or air. Nutrients recycled in winter spring carried forward to. Organic nutrients in dead biomass are recycled through decay and mineralization which regenerate the supply of available nutrients.
Into the soil nearby water and air. Because no plant roots to. Mineral cycles include the carbon cycle sulfur cycle nitrogen cycle water cycle phosphorus cycle oxygen cycle among others that continually.
The recycling of various nutrients takes place in the form of nutrient cycles. Nutrient Recycling 23 These nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material. Recycling is the process of making used or unwanted products into new remanufactured products.
Soil bacteria perform recycling of soil organic matter through different processes and as a result they produce and release into the soil inorganic molecules NH 4 NO 3 PO 4 3 CO 2 that can be consumed by plants and microorganisms to grow and perform their functions. In high amounts these nutrients are detrimental to aquatic ecosystem health because elevated nutrients promote excessive growth or blooms of algae and other nuisance species. A process in which organisms take waste materials break them down and make new materials from them using biological processes such as anaerobic digestion or photosynthesis.
The organic nutrients may then enter the food web and are eventually deposited as dead biomass. Not all of the building blocks required by plants are readily available and they must be carefully conserved within the ecosystem.
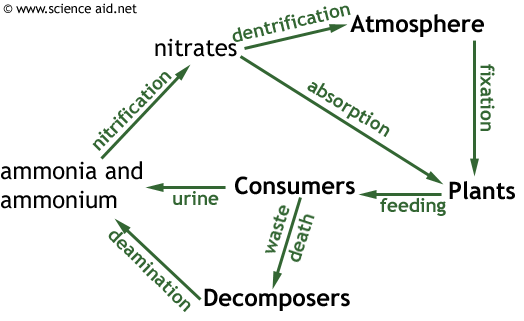
Nutrient Cycles Recycling In Ecosystems The Carbon And Nitrogen Cycles Scienceaid
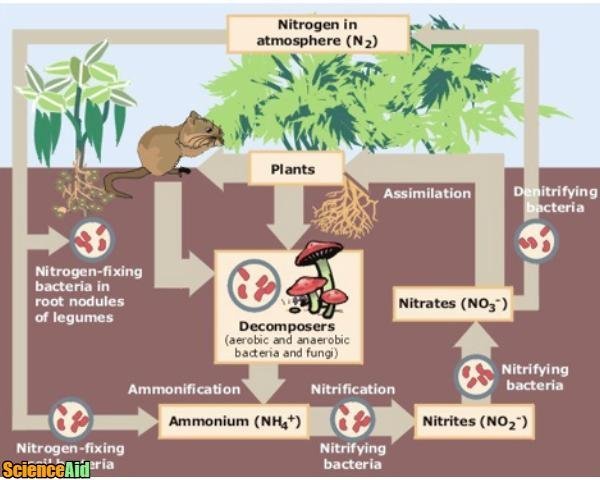
Nutrient Cycles Recycling In Ecosystems The Carbon And Nitrogen Cycles Scienceaid
Comments
Post a Comment